“Project Coast: The Darkest Secret of Apartheid South Africa”
What if you discovered a secret so dangerous, even speaking about it could land you in prison? In the tumultuous era of apartheid, the south African government was hiding a sinister secret that would shock the world. Behind closed doors, a team of scientists and military officials were working on a top-secret project that would push the boundaries of human endurance and morality. This is the story of Project coast, a clandestine operation that would leave a trail of devastation and death in its wake.
it’s the 1980s, and the apartheid regime is facing mounting international pressure and internal resistance. The government, desperate to maintain control, turns to unconventional methods to quash dissent and crush opposition. In the shadows, a secret project is born, codenamed “Project Coast.” Led by the enigmatic and brilliant scientist,Dr. Wouter Basson, a team of experts from various fields is assembled to develop a range of biological and chemical agents designed to disrupt and incapacitate the enemy – be it anti-apartheid activists, rival governments, or even their own population.
Dr. Basson, a charismatic figure with a reputation for innovative thinking, is the perfect candidate to lead this covert operation. A renowned chemist and botanist, he has a captivation with toxic plants and their potential applications. His team, comprising of experts in microbiology, biochemistry, and engineering, works tirelessly in a network of secret laboratories and facilities across south Africa. Their mission: to create a suite of deadly toxins, incapacitating agents, and mind-altering substances that can be used to eliminate threats to the apartheid regime.As Project Coast gains momentum, the scope of the operation expands. The team begins experimenting with a range of deadly toxins,including a highly potent botulinum-based agent and a genetically engineered bacterium designed to produce a lethal toxin. They also develop an array of incapacitating agents, such as a powerful sedative and a hallucinogenic substance meant to disorient and confuse. The possibilities seem endless, and the scientists are driven by a sense of excitement and curiosity.
Though, as the project advances, the lines between science and morality begin to blur. The team starts to test their creations on unsuspecting subjects, frequently enough using prisoners, dissidents, and even innocent civilians as guinea pigs. The results are devastating. Many test subjects suffer from severe symptoms, including paralysis, hallucinations, and even death.The scientists, fueled by a zeal for innovation and a disregard for human life, press on, convinced that their work will help maintain the apartheid regime’s grip on power.
But Project Coast is not just about creating deadly agents; it’s also about psychological warfare. The team begins exploring the use of mind-altering substances, including a truth serum and a psychoactive agent designed to induce euphoria or despair. The goal is to create a “chemical cosh” that can be used to extract facts, manipulate behavior, or simply break the spirit of their enemies. The implications are chilling, and the potential for abuse is limitless.
As the project reaches its zenith, the apartheid government begins to deploy these secret agents in various operations. Spies and assassins, armed with vials of deadly toxins and incapacitating substances, are sent to eliminate targets across the globe. The targets include anti-apartheid activists, journalists, and even government officials from rival countries. The message is clear: the apartheid regime will stop at nothing to maintain its grip on power.
However,as Project Coast gains notoriety,whispers of the secret project begin to leak into the public domain. Journalists, activists, and opposition leaders start to piece together the truth, and the evidence points to a massive conspiracy involving the highest echelons of the apartheid government. The international community is shocked and outraged, and demands for accountability grow louder.
In the late 1990s,as apartheid South Africa teeters on the brink of collapse,the truth about Project Coast finally begins to unravel.An examination by the South African Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC) exposes the extent of the project’s atrocities, and Dr. Wouter Basson is brought to trial for his role in the clandestine operation. The evidence presented at the trial is damning: documents, testimony from former scientists and agents, and even video footage of the secret laboratories and experiments.
The aftermath of Project Coast is marked by widespread condemnation and a sense of national shame. The South African government is forced to confront its dark past,and the apartheid era’s most notorious perpetrators are brought to justice. Dr. Basson, who had always maintained that his work was purely scientific and not intended for harm, is eventually acquitted, but his reputation is forever tarnished.The legacy of Project Coast serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific hubris and the blurring of moral boundaries. It highlights the devastating consequences of allowing governments and institutions to pursue secret agendas without accountability or oversight. As the world grapples with the challenges of emerging technologies and scientific advancements, the story of Project Coast serves as a reminder of the importance of ethics, transparency, and human rights.
the truth about Project Coast serves as a testament to the power of investigative journalism, activism, and the unyielding pursuit of justice. It’s a reminder that even in the darkest corners of history, there are always voices willing to speak out against injustice and fight for the truth.
#ProjectCoast #ApartheidSouthAfrica #biologicalwarfare #ChemicalAgents #MindControl #PsychologicalWarfare #TruthAndReconciliation #SouthAfricanHistory #InfographicStory #TrueStory #HistoryNerd #didyouknow #GlobalFigures #AfricanHistory #SouthAfricanSecrets #HiddenHistory #militaryexperiments #governmentprojects #ClassifiedSouthAfrica
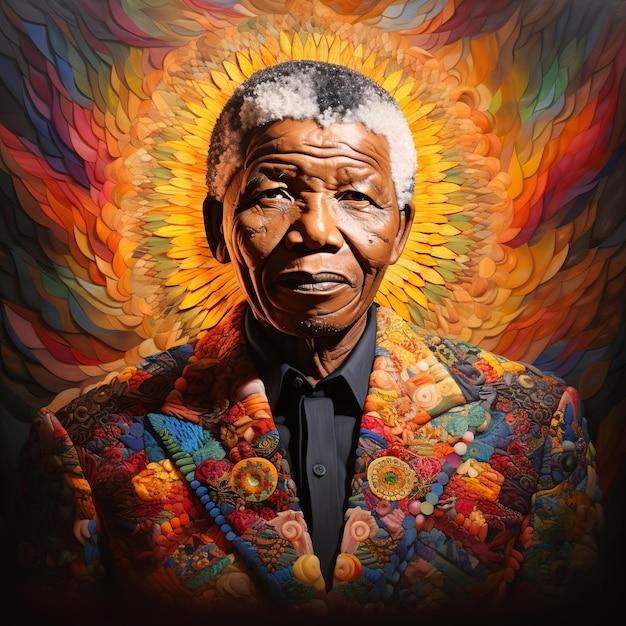
<img class="bimage_class" src="https://campusstore.co.za/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/dela-4.jpg" alt="“The Unyielding Spirit of Nelson Mandela: Uncovering the Turbulent Life of a Revolutionary leader”
Imagine a world where one man spent 27 long, arduous years in prison, only to emerge not as a bitter, broken soul, but as a beacon of hope and unity for a nation torn apart by decades of brutal oppression. This is the remarkable story of Nelson Mandela, a name that has become synonymous with courage, resilience, and the unwavering pursuit of justice. But who was this extraordinary individual, and what drove him to challenge the very fabric of a society that seemed persistent to crush his spirit? Born on July 18, 1918, in the small village of Mvezo, South Africa, Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela was raised in a world where tradition and culture were deeply intertwined with the harsh realities of colonialism and racism.
As a young boy, Mandela was fascinated by the stories of his ancestors, who had fought against the British colonial forces in the 19th century. His father, Gadla Henry Mphakanyiswa, was a local chief and a strong influence on Mandela’s early life, instilling in him a deep sense of pride and a commitment to serving his community. However, it was not until Mandela attended the University of Fort hare, a bastion of African nationalism and intellectual ferment, that he began to grasp the magnitude of the injustices perpetrated against his peopel. The University of Fort Hare was a hotbed of radical ideas and activism, and Mandela was drawn into a world of politics and resistance, where he met other like-minded individuals who shared his passion for challenging the status quo.
One of the most significant events that shaped Mandela’s early life was his involvement in the 1944 student’s Representative Council (SRC) protest, which led to his expulsion from the university. This experience,though initially disheartening,marked a turning point in Mandela’s journey,as he began to see the value of collective action and the power of resistance. He went on to complete his degree in absentia and later enrolled in the University of Witwatersrand, where he became increasingly involved in the African National Congress (ANC), a organization dedicated to fighting for the rights of black South Africans. As Mandela’s involvement in the ANC deepened, he became part of a growing movement of young activists, including Oliver Tambo and Walter Sisulu, who were determined to challenge the apartheid regime through non-violent resistance.
The 1948 election in South Africa, which saw the National Party come to power on a platform of apartheid, marked a dark and ominous turning point in the country’s history. The new government, led by D.F. Malan, began to entrench the racist policies that would define the apartheid era, stripping black South Africans of their basic rights and freedoms. Mandela, along with other ANC leaders, responded by escalating their resistance, organizing protests, boycotts, and civil disobedience campaigns. Though, as the apartheid regime grew increasingly brutal, Mandela and his fellow activists realized that non-violent resistance alone might not be enough to bring about change.
The Sharpeville massacre in 1960,in which police opened fire on a peaceful protest,killing 69 people and wounding hundreds more,marked a watershed moment in the struggle against apartheid. The ANC, faced with the regime’s escalating violence, made the difficult decision to adopt armed struggle as a means of resistance. Mandela, now a key leader in the ANC, traveled to Algeria and other parts of Africa, receiving military training and building alliances with other anti-colonial movements. Upon his return to South Africa, he co-founded the ANC’s armed wing, Umkhonto we Sizwe (Spear of the Nation), and began to organize a campaign of sabotage against government targets.
Though, Mandela’s new path was not without its risks. In August 1962, he was arrested and charged with inciting workers to strike and leaving the country without a passport. The subsequent trial, known as the Rivonia trial, was a sham, with the government determined to secure a guilty verdict. Mandela’s famous statement from the dock, in which he declared his willingness to sacrifice his life for the cause of freedom, electrified the nation and galvanized international opposition to apartheid. the trial ended with Mandela being sentenced to life imprisonment, along with other ANC leaders.
The years that followed were some of the darkest in South African history. Mandela, along with other prisoners on Robben Island, was subjected to hard labor, physical brutality, and psychological torture. Yet, even in the face of such unimaginable hardship, Mandela’s spirit remained unbroken. He continued to advocate for the rights of his fellow prisoners, using his time in prison to cement his reputation as a leader and a unifying force.As the years turned into decades, Mandela became an international symbol of resistance against apartheid, with his name becoming synonymous with the struggle for justice and equality.
The 1980s saw a significant shift in the global landscape, with the anti-apartheid movement gaining momentum and international pressure on the South African government mounting. As the regime faced increasing isolation and economic sanctions, the internal resistance movement, fueled by Mandela’s leadership and vision, continued to grow.In 1990, after 27 long years in prison, Mandela was finally released, his freedom sparking widespread euphoria and marking a new era in South Africa’s history.
The years that followed were not without their challenges. As Mandela worked alongside President F.W. de klerk to dismantle apartheid and transition the country to democracy, he faced opposition from both within and outside the ANC. Though, through his unwavering commitment to reconciliation and his willingness to engage with his former oppressors, Mandela helped to navigate the country through a fragile and frequently enough tumultuous period.In 1994,South Africa held its first democratic elections,with Mandela becoming the country’s first black president.
As president, Mandela worked tirelessly to heal the wounds of the past, establishing the Truth and Reconciliation Commission to confront the atrocities committed during apartheid. He also implemented policies aimed at addressing the socio-economic disparities created by decades of racist rule. though his presidency was not without its challenges, Mandela’s leadership and vision helped to chart a new course for South Africa, one that prioritized justice, equality, and reconciliation.
Nelson Mandela’s legacy extends far beyond his own country. His life and work have inspired movements for justice and human rights around the world. As we reflect on his remarkable story, we are reminded that even in the face of seemingly insurmountable adversity, the human spirit can prevail, and that one person, driven by conviction and courage, can change the course of history.Mandela’s story is a testament to the power of resilience, compassion, and the unwavering commitment to a cause greater than oneself.
#InfographicStory #WorldHistory #HistoricalEvents #DidYouKnow #truestory #HistoryNerd #GlobalFigures #Apartheid #SouthAfrica #NelsonMandela #MandelaLegacy #AntiApartheidMovement #FreedomFighter #HumanRights #Reconciliation #Democracy #Leadership #Inspiration #Motivation #SocialJustice #EqualityForAll #NeverGiveUp”>