“The Sinister Secrets of Project Coast: South Africa’s Most Classified Experiment”
What if you discovered a secret so perilous, even speaking about it could land you in prison? In the depths of apartheid-era South Africa, a clandestine government project was underway, shrouded in mystery and deceit. Project Coast, a covert military experiment, would push the boundaries of human endurance, ethics, and morality, leaving a trail of devastating consequences that would haunt the nation for decades to come.
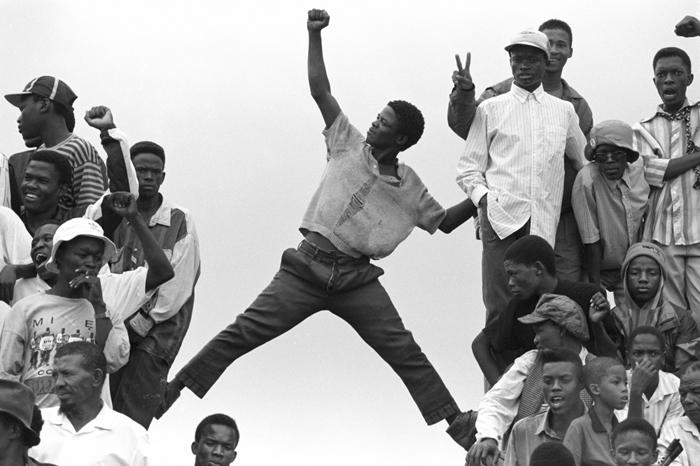
It’s 1985 in Pretoria, and behind locked gates, government scientists are testing something the world isn’t ready for. The apartheid regime, desperate to maintain control and quell growing dissent, had initiated Project Coast, a secret research and development program aimed at creating chemical and biological agents to be used against anti-apartheid activists, protesters, and even foreign enemies. The project’s existence was a closely guarded secret, known only to a select few high-ranking officials and scientists.
The brainchild of the South African Defense Force (SADF), Project Coast was led by Dr. Wouter Basson, a brilliant and enterprising chemist who would become the architect of the program’s most sinister experiments.Basson, a former member of the South African Army’s chemical and biological warfare unit, had a reputation for being ruthless and cunning, with a zeal for innovation that bordered on obsession. He would stop at nothing to achieve his goals, including experimenting on human subjects.
As Project Coast gained momentum, Basson assembled a team of skilled scientists, engineers, and technicians from various disciplines, including chemistry, biology, and pharmacology. Together, they worked tirelessly to develop a range of deadly agents, from nerve gas and toxins to biological warfare agents. The team’s work was shrouded in secrecy, with researchers often working under pseudonyms and in isolated facilities.
one of the most shocking aspects of Project Coast was the use of human test subjects. Unwittingly, hundreds of people, including anti-apartheid activists, prisoners, and even some of the scientists’ own colleagues, where exposed to the deadly agents. These experiments were frequently enough conducted in secret, with subjects being monitored and observed in specially designed facilities. Many test subjects suffered from severe health complications, including respiratory problems, skin lesions, and even death.
The project’s methods were brutal and inhumane. Test subjects were often given intentionally misleading data about the nature of the experiments, and some were even coerced into participating through threats or promises of financial rewards. The true extent of the experiments remains unknown,as many records were destroyed or remain classified to this day.
As Project Coast continued to expand, the apartheid regime grew increasingly paranoid, fearing that the project’s existence would be exposed to the international community. To maintain secrecy, the government established a complex web of cover stories, front companies, and shell organizations. These tactics allowed the project to operate with relative impunity, shielded from scrutiny by the outside world.
However,the consequences of Project Coast would eventually come back to haunt the apartheid regime. In the late 1980s, rumors of the project’s existence began to circulate, sparking international outrage and condemnation. As protests mounted, the government was forced to acknowledge the project’s existence, albeit in a limited and heavily sanitized form.
In 1993, with the apartheid regime on the brink of collapse, the South African government established the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC) to investigate human rights abuses and provide a platform for victims to share their stories. The TRC’s hearings revealed shocking testimony about Project Coast, including the use of human test subjects and the development of deadly agents.
The aftermath of Project Coast was marked by widespread outrage, recriminations, and a deep-seated sense of shame. Many of those involved in the project, including Dr.Basson, faced prosecution and public scrutiny. In 1999, Basson was found guilty of murder and other crimes related to Project Coast, but he was released on bail pending an appeal. The project’s legacy continues to cast a long shadow over South Africa, serving as a stark reminder of the dangers of unchecked power and the importance of accountability.
The story of Project Coast serves as a chilling reminder of the darkest aspects of human nature, where the pursuit of power and control can lead even the most well-intentioned individuals down a path of destruction and chaos. As we reflect on this dark chapter in South African history, we are reminded of the importance of openness, accountability, and the protection of human rights.
In the years since Project Coast,South Africa has made significant strides in promoting transparency and accountability,including the establishment of the TRC and the implementation of robust human rights protections. However, the legacy of Project Coast continues to serve as a cautionary tale, reminding us of the dangers of unchecked power and the importance of vigilance in protecting human rights.
#SouthAfricanSecrets #HiddenHistory #MilitaryExperiments #GovernmentProjects #ClassifiedSouthAfrica #InfographicStory #TrueStory #AfricanHistory #ProjectCoast #ApartheidRegime #ChemicalAndBiologicalWarfare #HumanRightsAbuses #TruthAndReconciliationCommission #AccountabilityMatters #TransparencyIsKey
<img class="bimage_class" src="https://campusstore.co.za/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/andela.jpg53f2.jpg" alt="The Unyielding Spirit of Nelson Mandela: A Fight Against Apartheid
Imagine a world where being born with a certain skin color could mean the difference between living a life of freedom and being condemned to a life of oppression. This was the harsh reality of apartheid South Africa, a regime that was as ruthless as it was pervasive. But amidst the darkness, a beacon of hope emerged in the form of a man who would stop at nothing to bring down the oppressive government and fight for the rights of his people. His name was Nelson Mandela, and his story is one of unwavering determination, unrelenting passion, and a refusal to back down in the face of overwhelming adversity.Born on July 18, 1918, in the small village of Mvezo, South Africa, nelson Mandela was raised in a customary Thembu family. His early life was marked by a deep connection to his African heritage and a strong sense of justice, instilled in him by his mother and the community around him. As he grew older, Mandela became increasingly aware of the injustices that plagued his country, especially the system of apartheid, which had been entrenched as the early 20th century.Apartheid, meaning “separateness” in Afrikaans, was a complex system of laws and social norms that kept black South Africans in a state of subjugation, denying them basic rights, education, and economic opportunities.
Mandela’s journey into the world of politics began during his time at the University of Fort Hare, where he was exposed to the ideas of African nationalism and became involved with the African National Congress (ANC). The ANC, founded in 1912, was a organization dedicated to fighting for the rights of black South Africans, and it was here that Mandela would meet some of the key figures who would shape his future. As the apartheid regime tightened its grip on the country, Mandela became increasingly radicalized, eventually joining the ANC’s Youth League and rising through the ranks to become one of its leading figures.
the 1950s and 1960s were tumultuous times in South Africa, with the apartheid government responding to growing resistance with brutal force. Mandela, along with other ANC leaders, was arrested multiple times for his activism, but he continued to organize protests and demonstrations, pushing for a united front against the government. The turning point came in 1960, when the Sharpeville Massacre occurred, leaving 69 unarmed black protesters dead at the hands of the police.The event marked a significant escalation in the conflict, and Mandela realized that armed resistance might be the only way to bring about change.
In 1961, Mandela co-founded the ANC’s armed wing, Umkhonto we Sizwe (Spear of the Nation), with the aim of sabotaging government infrastructure and installations. The decision was not taken lightly, and it marked a significant shift in Mandela’s strategy, from nonviolent resistance to armed struggle. The years that followed were marked by a series of high-profile sabotage operations, as well as a cat-and-mouse game between Mandela and the government. In 1962, he was arrested and sentenced to five years in prison for inciting workers to strike and leaving the country without a passport.
However,it was during his trial in 1964,known as the Rivonia Trial,that Mandela would make his most enduring statement. Accused of treason alongside other ANC leaders, Mandela used the dock to deliver a powerful speech, affirming his commitment to the fight against apartheid and his willingness to sacrifice his life for the cause. “I have fought against white domination, and I have fought against black domination. I have cherished the ideal of a democratic and free society in which all persons live together in harmony and with equal opportunities,” he declared. The speech, which would become known as “I Am Prepared to Die,” was a defining moment in Mandela’s life and a rallying cry for the anti-apartheid movement around the world.
The Rivonia Trial ended with Mandela being sentenced to life imprisonment, along with several other ANC leaders. For the next 27 years, Mandela would be held in harsh conditions, first on Robben Island and later in Pollsmoor Prison. Despite the isolation, Mandela’s spirit remained unbroken. He continued to advocate for the rights of prisoners and became a symbol of resistance against apartheid, both within South Africa and globally.
The international community began to take notice of Mandela’s plight, and pressure mounted on the south African government to release him. By the late 1980s, the apartheid regime was facing increasing isolation and internal unrest. In 1990, after months of secret negotiations, President F.W. de Klerk finally lifted the ban on the ANC and announced Mandela’s release from prison. The event was met with jubilation around the world,and Mandela,now an international icon,was poised to play a crucial role in the transition to democracy.
The years that followed were marked by a complex and often tense negotiation process between the apartheid government, the ANC, and other stakeholders. Mandela worked tirelessly to bring about a peaceful transition,often displaying a level of pragmatism and forgiveness that surprised his critics. In 1994, South Africa held its first multiracial democratic elections, and Mandela became the country’s first black president. His presidency was marked by efforts to heal the wounds of apartheid, including the establishment of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission, which aimed to provide a platform for victims and perpetrators to share their stories.
Mandela’s legacy extends far beyond his presidency. he became a global symbol of hope and reconciliation, earning the Nobel Peace Prize in 1993 for his efforts to bring peace and democracy to South Africa. His story has inspired countless people around the world, from civil rights activists to ordinary citizens fighting against injustice. Today, Mandela’s name is synonymous with courage, forgiveness, and the unwavering commitment to fighting for what is right.
As we look back on Mandela’s life, we are reminded of the power of the human spirit to overcome even the most daunting challenges. His story is a testament to the impact one person can have on the world, and a powerful reminder that even in the darkest of times, there is always hope for a better future.
#NelsonMandela #Apartheid #SouthAfrica #MandelaLegacy #FightForFreedom #InfographicStory #WorldHistory #HistoricalFigures #TrueStory #HistoryNerd #globalicons #AntiApartheidMovement #RivoniaTrial #RobbenIsland #Democracy #Reconciliation #NobelPeacePrize #MandelaStory #LegacyOfCourage”>